Corneal Topography
Introduction
Corneal topography is a revolutionary diagnostic tool in ophthalmology that allows eye care professionals to precisely map the surface curvature of the cornea. This non-invasive procedure provides invaluable insights into various eye conditions, enabling accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans. Let's delve into the depths of corneal topography to understand its significance and applications in eye care.

Understanding Corneal Topography
The cornea, the transparent outer layer of the eye, plays a crucial role in focusing light onto the retina, facilitating clear vision. Irregularities in its shape can lead to refractive errors such as astigmatism, myopia, and hyperopia, as well as conditions like keratoconus. Corneal topography involves the use of specialized instruments to create a detailed map of the cornea's surface curvature, akin to creating a topographic map of terrain.
What to Expect During a Corneal Topography Scan
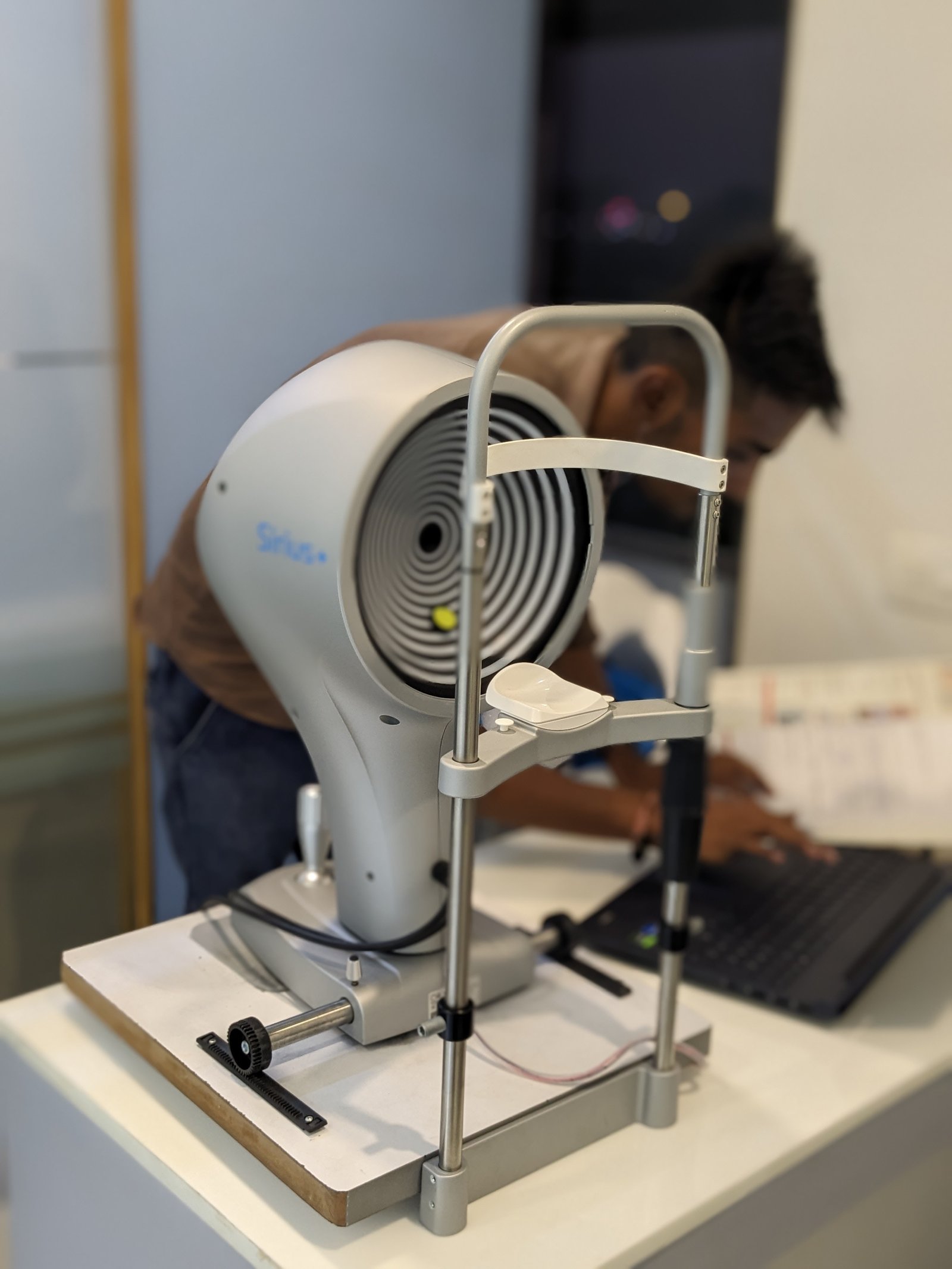
- You will be seated facing a large bowl with lighted circles inside it. The chin and forehead rests keep your head secure to get the clearest images.
- You will be asked to stare at a fixed target in the bowl while the pictures are taken.
- The scan only takes a few seconds, but it may need to be repeated a few times.
- Getting a corneal topography is painless, as nothing touches your eye during the scan.
Your doctor may look over the images with you during the exam or at a follow-up exam.
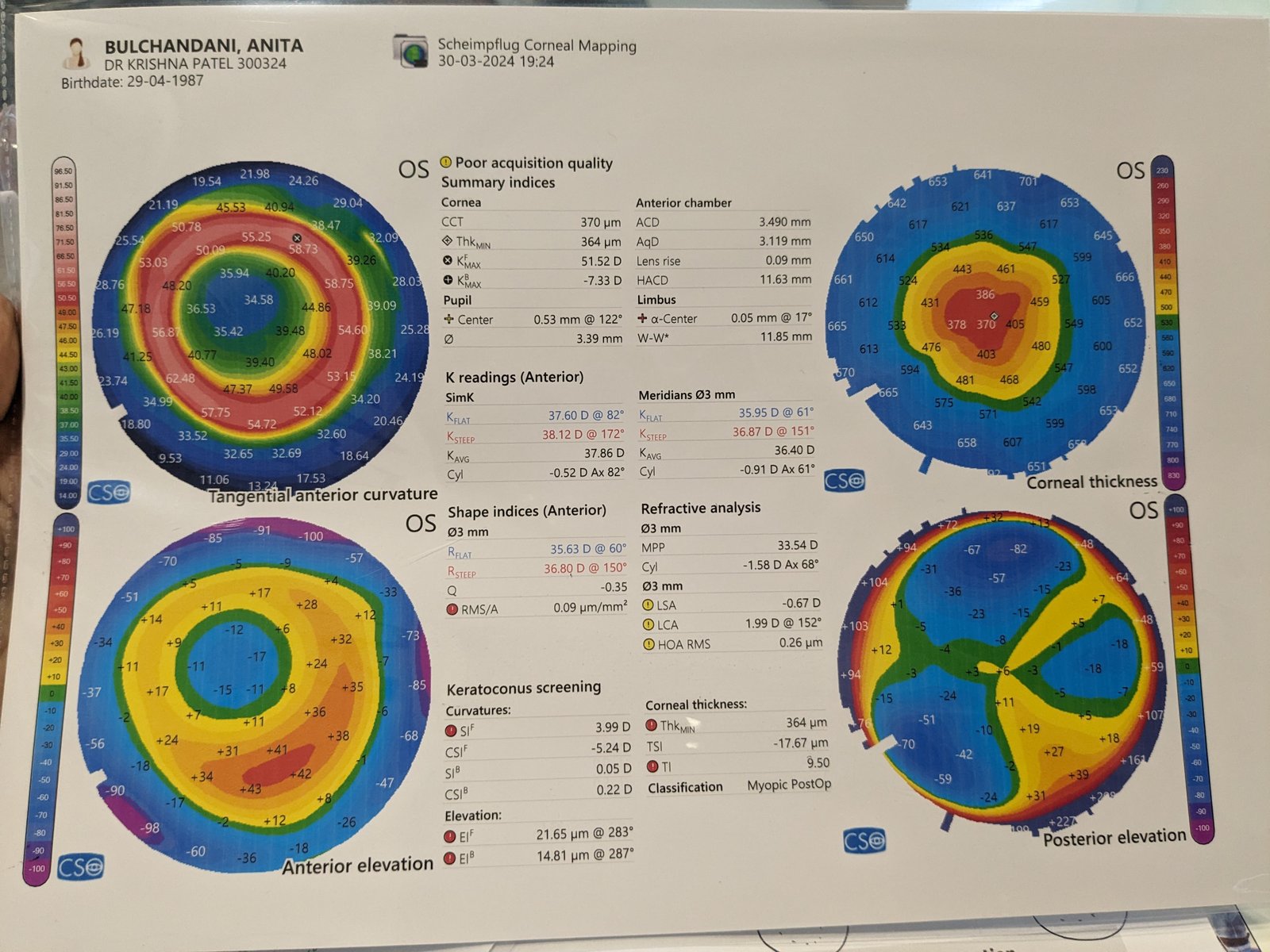
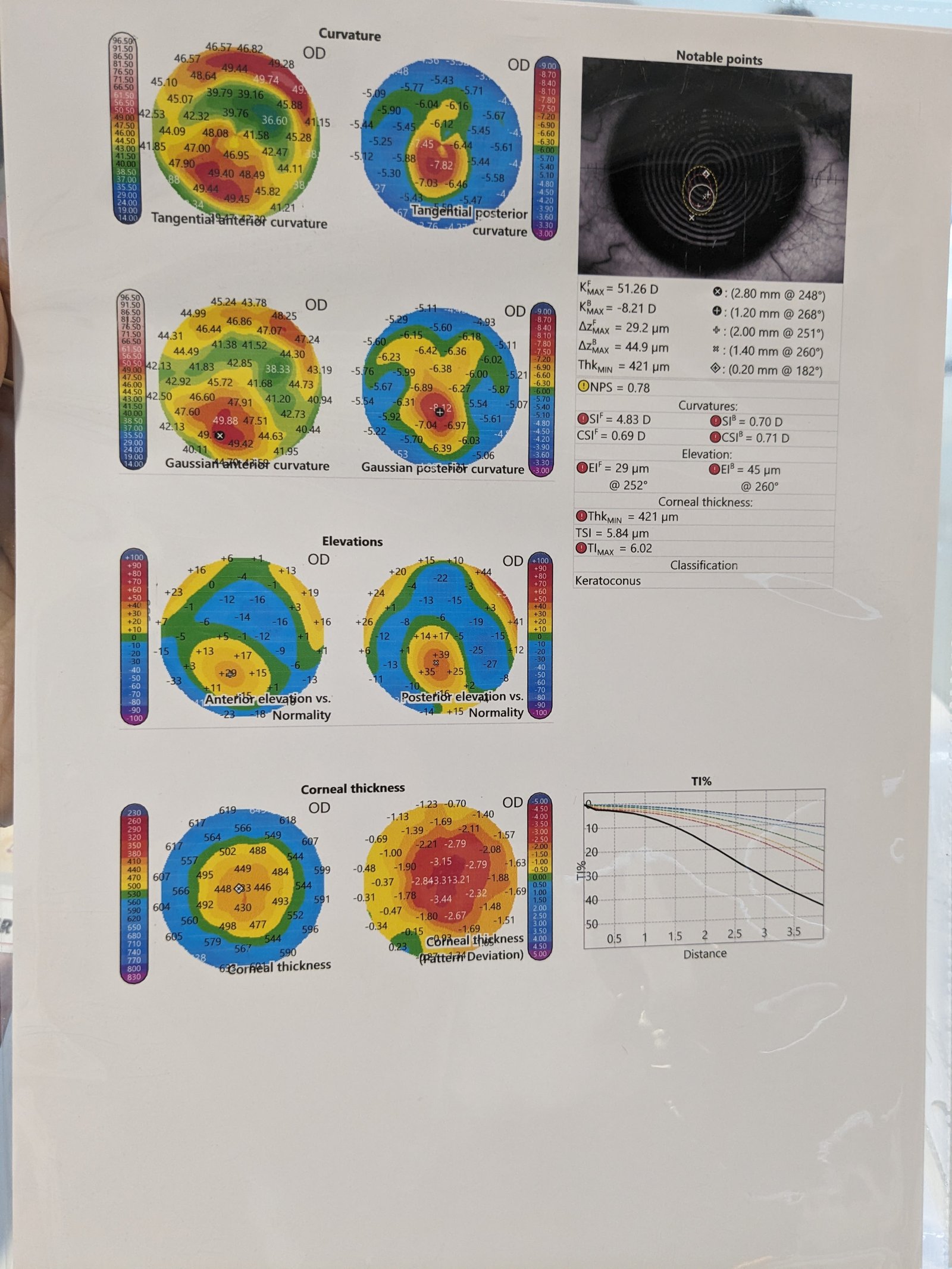
A sample image of what a corneal topography scan might look like.
Uses
Corneal topography and tomography is most commonly used for the following purposes
- Refractive surgery : To screen candidates for normal corneal shape, patterns and ruling out suspicious or keratoconic patterns . Post operatively , imaging can help to assess the dioptric change created at corneal level ( thus the effective change in the cornea) , ruling out de-centered or incomplete ablation , post excimer ectasia or other changes.
- Keratoconus : Early screening of keratoconus suspects is one of the most useful roles of corneal imaging. Early keratoconus and suspects look normal on slit lamp examination ,and the central keratometry (3 mm) gives only a limited assessment. Therefore imaging has become the gold standard in screening keratoconus suspects. In cases with established keratoconus, the role of topography and tomography is paramount for monitoring progression and doing a timely collagen cross linking , and in hard contact lens fittings.
- Post surgery astigmatism : Post cataract surgery and post keratoplasty corneal astigmatism can be studied with the topographer and selective suture removal or other interventions can be planned.
- Surgical planning in cases with corneal astigmatism : Limbal relaxing incisions and other methods of topography guided incision placement are used by surgeons to reduce post operative astigmatism.
- Effect of corneal and ocular surface disorders : Disorders such as pterygium , limbal dermoids, corneal scars, or degenerations can cause changes in the corneal curvature and irregular astigmatism.
- Other uses : Contact lens fitting , incision placement and intrastromal ring placement in keratoconus , monitoring of ocular vs corneal wavefront.
How Does Corneal Topography Help with Surgery?
- Refractive surgery. During refractive surgery like LASIK, the shape of the cornea is changed to correct refractive errors like myopia (nearsightedness). A topography scan helps the surgeon understand how to precisely reshape the cornea.
- Cataracts. When cataracts make the eye’s natural lens cloudy, it is replaced with an intraocular lens (IOL) during cataract surgery. Corneal topography helps surgeons select the right IOL in some cases.
- Corneal transplants. After a corneal transplant, a surgeon may use corneal topography to help a patient heal correctly. The images help assess which stitches should be removed and when based on the shape of the cornea.
- Corneal cross-linking. Corneal cross-linking surgery helps strengthen a cornea with keratoconus. A topography scan may be done to see if this surgery is needed. After surgery, scans are done to monitor the eye.




